Webhooks
Webhooks allow you to POST custom payloads to any endpoint in your own infrastructure or a third party provider. In a nutshell, you can:
- Create a custom URL by adding in authentication tokens or other secrets.
- Create a custom payload body using any environment variables and specific instance variables per event. Note: that means that if you are attaching the webhook to a Group, you will be able to access Group-level variables, too.
- Debug and test the webhook in the editor by sending test messages.
Using variables
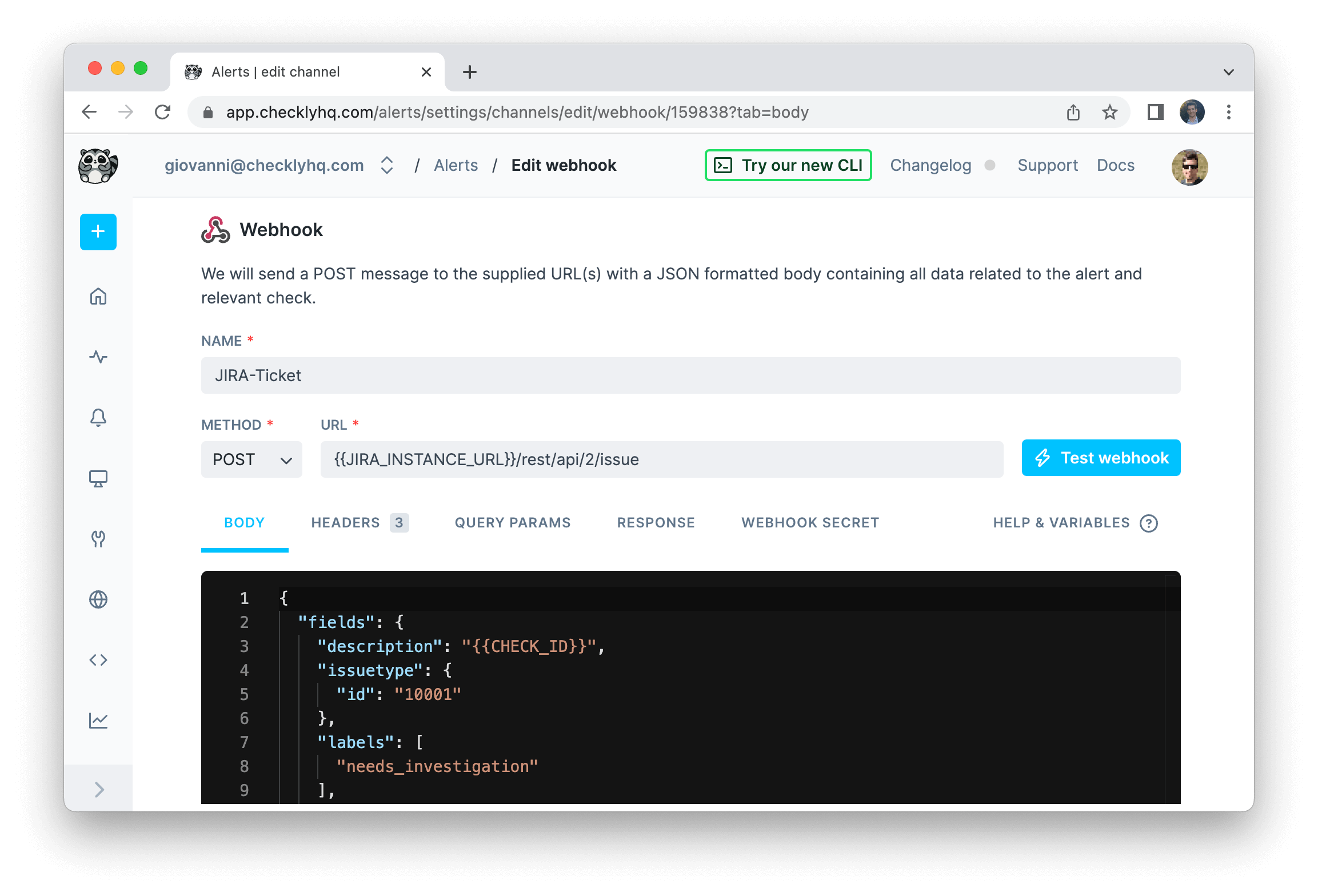
The example above shows a webhook configured to create a Jira ticket on each event. Notice the following:
- We use the variable
JIRA_INSTANCE_URLin the URL. We previously stored this variable in the environment variables section. - We use the variable
CHECK_IDin the payload. This is one of many event-based variables that will change with each call. See below for the complete list.
In both cases we use the familiar Handlebars templating braces, i.e. {{ }} to insert the variable.
{{{USER_API_KEY}}}You can use the following event-related variables in both URL and payload.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
CHECK_NAME |
Full name of the check |
CHECK_ID |
The UUID of the check |
CHECK_TYPE |
The check type, i.e. API or BROWSER. |
ALERT_TITLE |
Human readable title, e.g. ‘Check “My API check” has failed’ |
ALERT_TYPE |
Type of alert, either “ALERT_FAIL”, “ALERT_RECOVERY”, “ALERT_DEGRADED” or “ALERT_DEGRADED_RECOVERY” |
CHECK_RESULT_ID |
The UUID of the result that triggered this message |
RESPONSE_TIME |
The reported response time for this result |
API_CHECK_RESPONSE_STATUS_CODE |
The response status code, e.g. 200. Only populated for API checks. |
API_CHECK_RESPONSE_STATUS_TEXT |
The response status text, e.g. “OK”. Only populated for API checks. |
RUN_LOCATION |
The location where the check ran, i.e. “N. California” |
RESULT_LINK |
The full link to the check result |
SSL_DAYS_REMAINING |
How many days remain on the SSL certificate. For ALERT_SSL only. |
SSL_CHECK_DOMAIN |
The domain of the SSL certificate. For ALERT_SSL only. |
STARTED_AT |
The ISO timestamp from when this check run started |
TAGS |
An array of tags assigned to the check. Have a look at our Opsgenie example below on how to render this to a JSON array. |
GROUP_NAME |
The name of the group, if the check belongs to one. |
Using Handlebars helpers
We’ve extended the Handlebars templating system with some handy helpers to make our webhooks even more powerful.
| helpers | description |
|---|---|
{{REGION}} |
Resolves to the AWS region name, i.e. us-east-1. |
{{$UUID}} |
Generates a random UUID/v4, i.e. 9b1deb4d-3b7d-4bad-9bdd-2b0d7b3dcb6d. |
{{$RANDOM_NUMBER}} |
Generates a random decimal number between 0 and 1000, i.e. 345. |
{{moment}} |
Generates a date or time using moment.js and allows for formatting:
|
A practical example of using the {{moment}} helper would be setting the pagination options on a typical API endpoint:
GET https://api.acme.com/events?from={{moment "last week" "X"}}&to={{moment "X"}}
You can find the full list of helpers in the README.md file of the underlying library we are using. For a full overview of date formatting option, check the moment.js docs.
You can also use conditional helpers like {{#eq}} statements. Here is an example:
{
"message": "Check is {{#eq ALERT_TYPE 'ALERT_FAILURE'}}DOWN{{/eq}} {{#eq ALERT_TYPE 'ALERT_RECOVERY'}}UP{{/eq}}"
}
The above webhook body uses the {{#eq}} helper to execute the logic
If the ALERT_TYPE variable equals ‘ALERT_FAILURE’, print ‘DOWN’, if it equals ‘ALERT_RECOVERY’ print ‘UP’
So in the case of a failure event, the body would render to:
{
"message": "Check is DOWN"
}
Two clear benefits here:
- You only need to create one webhook to inform a 3rd party system.
- You can translate Checkly terms to your 3rd party tool’s term for the same concept, i.e. the “up status” of a check.
You can find the full list of helpers in the README.md file of the underlying library we are using.
Webhook secrets
You can validate each webhook we deliver to your endpoint(s). Using the optional webhook secret, you can:
- Check if the webhook was sent by Checkly.
- Check if the payload was not altered in any way during transmission.
When you create a webhook secret, we proceed to use that secret token to cryptographically sign the webhook payload using
the SHA256 hash algorithm. We add the resulting hash to the HTTP header x-checkly-signature on each webhook.
On the receiving end, you can then use the value of the x-checkly-signature header to assert the validity and authenticity
of the webhook and its payload.
Have a look at the code examples below on how to use the header and your favourite web framework.
// We store the webhook secret in an environment variable called CHECKLY_WEBHOOK_SECRET
const app = require('express')();
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const crypto = require('crypto');
function isVerifiedPayload (payload, signature) {
const secret = process.env.CHECKLY_WEBHOOK_SECRET
const hmac = crypto.createHmac('sha256', secret)
const digest = hmac.update(payload).digest('hex')
return crypto.timingSafeEqual(Buffer.from(digest), Buffer.from(signature))
}
app.post('/webhook', bodyParser.json({ type: 'application/json' }), (request, response) => {
const signature = request.headers['x-checkly-signature'];
const payload = JSON.stringify(request.body)
if (isVerifiedPayload(payload, signature)) {
console.log('Signature is valid')
response.status(200).send();
} else {
console.error('Signature does not match')
response.status(400).send();
}
});
app.listen(4242, () => console.log('Running on port 4242'));
# We store the webhook secret in an environment variable called CHECKLY_WEBHOOK_SECRET
require 'sinatra'
set :port, 4242
post '/webhook' do
signature = request.env['HTTP_X_CHECKLY_SIGNATURE']
payload = request.body.read
digest = OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest(OpenSSL::Digest.new('sha256'), ENV['CHECKLY_WEBHOOK_SECRET'], payload)
if Rack::Utils.secure_compare(digest, signature)
status 200
return
else
status 400
return
end
end
# This example assumes you use Django
import hmac
from hashlib import sha256
from django.conf import settings
from django.http import HttpResponse, HttpResponseBadRequest
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
from django.utils.encoding import force_bytes
import json
@csrf_exempt
def webhook(request):
signature = request.META.get('HTTP_X_CHECKLY_SIGNATURE')
mac = hmac.new(settings.CHECKLY_WEBHOOK_SECRET.encode('utf-8'), msg=request.body, digestmod=sha256)
print(mac.hexdigest())
if not hmac.compare_digest(mac.hexdigest(), signature):
return HttpResponseBadRequest()
return HttpResponse()
Webhook retries
Checkly will retry your webhook up to 5 times if we get an HTTP response higher than 399, e.g. a 404 or 503. Each retry
is backed off 20 seconds for a total retry period of 5 * 20 = 100 seconds.
This means that for checks on a 1 minute schedule, there is a potential overlap between a failure alert and recovery alert. For this
reason every webhook we send has a timestamp in the x-checkly-timestamp header. You can use this timestamp on the receiving
end to ignore any webhooks that come in “late”.
Webhook examples
The following examples give an idea how to integrate Checkly with 3rd party alerting and issue tracking systems.
OpsGenie
You can create an OpsGenie alert by POST-ing the following body
{
"message": "{{ALERT_TITLE}}",
"description": "{{ALERT_TYPE}} <br>{{STARTED_AT}} ({{RESPONSE_TIME}}ms) <br>{{RESULT_LINK}}",
"tags": [{{#each TAGS}} "{{this}}" {{#unless @last}},{{/unless}} {{/each}}]
}
to the OpsGenie alerts API endpoint
https://{{OPSGENIE_API_KEY}}@api.opsgenie.com/v2/alerts
Or you can add the OpsGenie API key in the headers, e.g.
Authorization: GenieKey {{OPSGENIE_API_KEY}}
This is an example of a full alert body:
{
"message": "{{ALERT_TITLE}}",
"description": "{{ALERT_TYPE}}: {{CHECK_NAME}} <br>{{STARTED_AT}} ({{RESPONSE_TIME}}ms) <br>{{RESULT_LINK}}",
"responders": [
{
"id":"4513b7ea-3b91-438f-b7e4-e3e54af9147c",
"type":"team"
}
],
"tags": ["Critical", "Production"],
"priority":"P1",
"note": "Location: {{RUN_LOCATION}}"
}
In case you would like different teams to be responsible for different Check Groups, you could add a CHECK_GROUP_TEAM variable with a different value for each Group, then modify the above snippet with the following:
"responders": [
{
"id":"{{CHECK_GROUP_TEAM}}",
"type":"team"
}
]
PagerDuty
Given an existing service on your PagerDuty account, create an incident for it by posting the following body
{
"incident": {
"type": "incident",
"title": "{{ALERT_TITLE}}",
"service": {
"id": "<YOUR_SERVICE_ID_FROM_PAGERDUTY>",
"type": "service_reference"
},
"body": {
"type": "incident_body",
"details": "Check {{CHECK_NAME}} with ID {{CHECK_ID}} has failed from location {{RUN_LOCATION}}. See check result for details: {{RESULT_LINK}}"
}
}
}
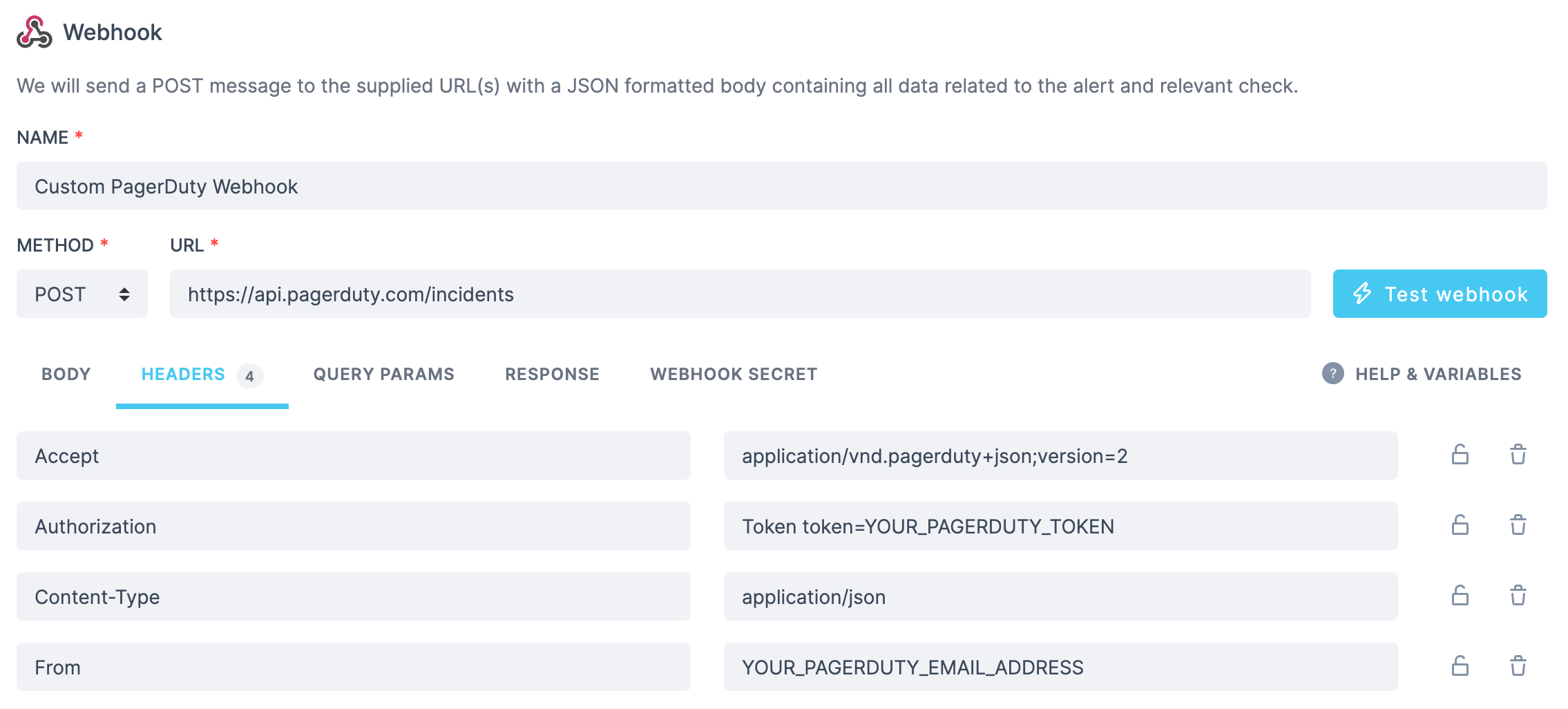
to https://api.pagerduty.com/incidents. You will need to set the following headers:
Pushover
Send a message using Pushover by posting this body:
{
"token":"YOUR_SECRET_TOKEN_FROM_PUSHOVER",
"user":"YOUR_USER_FROM_PUSHOVER",
"title":"{{ALERT_TITLE}}",
"html":1,
"priority":2,
"retry":30,
"expire":10800,
"message":"{{ALERT_TYPE}} <br>{{STARTED_AT}} ({{RESPONSE_TIME}}ms) <br>{{RESULT_LINK}}"
}
Trello
You can create a Trello card using just the URL and no payload:
https://api.trello.com/1/cards?idList=5b28c04aed47522097be8bc4&key={{TRELLO_KEY}}&token={{TRELLO_TOKEN}}&name={{CHECK_NAME}}
SSL alert
You can send your SSL alerts using webhooks. Using the following body:
{
"message": "{{ALERT_TITLE}}",
"link":"{{RESULT_LINK}}"
}
Will yield the following output, where we customize the ALERT_TITLE to include the domain and the days remaining till your
certificate expires.
{
"message": "The SSL certificate for api.checklyhq.com will expire in 14 days",
"link": "http://app-test.checklyhq.com/checks/08437f9c-df8c-45ed-975a-a3f9e24d626d"
}
Twilio
You can configure a webhook to POST to a JavaScript snippet running in a Twilio Function. This code receives the Checkly webhook JSON, then triggers a Twilio “Flow execution”:
//"From" is the sender phone number
//"To" is the receiver phone number
exports.handler = async function (context, event, callback) {
const { From, To, Event, Link } = event;
const client = context.getTwilioClient();
try {
const execution = await client.studio.flows(FLOW_SID)
.executions
.create({ to: To, from: From, parameters: { Event, Link } })
console.log(`Created execution ${execution.sid}`);
return callback(null, "OK");
} catch (error) {
return callback(error);
}
};
Jira
A webhook can be used to create a new issue on Jira via the Jira API, for example in the case of a previously passing check that switches to failing state.
We will be creating a POST request to {{JIRA_INSTANCE_URL}}/rest/api/2/issue, where the content of your JIRA_INSTANCE_URL environment variable would look something like https://your-jira-instance-name.atlassian.net.
The required headers will be:
Authorization: <YOUR_JIRA_BASIC_AUTH>
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json
An example body could look as follows:
{
"fields": {
"description": "{{RESULT_LINK}}",
"issuetype": {
"id": "10001" // your Jira issue type id
},
"labels": [
"needs_investigation"
],
"project": {
"key": "ABC" // your Jira project key
},
"summary": "{{ALERT_TITLE}}"
}
}
Last updated on September 5, 2024. You can contribute to this documentation by editing this page on Github